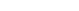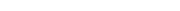When an 80 bhp Version appeared in 1938 (327/28) to meet demands for performance and sportiness, strangely enough sales for the basic 327 also picked up. A total of 1124 convertibles and 179 coupes were built. In May 1941, the last coupe was supplied to the Brazilian consul-general de Louza-Ribeiro in Hamburg.
Like its predecessors, which were also equipped with a 2-liter engine (BMW 320, 321 and 326), the 327 had a low slung box-section chassis, on which car bodies manufactured by “Ambi-Budd” coachworks in Berlin-Johannisthal were used. “Ambi-Budd” and “Autenrieth” in Darmstadt were BMW’s largest suppliers of car bodies in the 1930s.
“Hurth” and “ZF” supplied the four-speed transmission (with freewheel facility in first and second gear). The drive ratio was identical in both types, and the differences in the individual gears were minor. What was different was how the doors were hinged — at the front in the convertible and at the back in the coupe.
After the dismantling of “Ambi-Budd”, the BMW chassis tools of the 321, 326 and 327 types went to “Awtowelo” in East Germany. The Russians and East German successor EMW (Eisenacher Motoren Werk) manufactured 491 BMW 327 descendants between 1952 and 1954. The EMW 327-3, an attractive coupe with a large rear window, was also manufactured.
It had many devotees amongst the leaders of the Third Reich, the 327 sports convertible became, in its postwar model, a Status Symbol for loyal and prominent Socialist Party comrades. Fans of Veteran BMWs consider the 327 to be one of the most beautiful convertibles of its time.